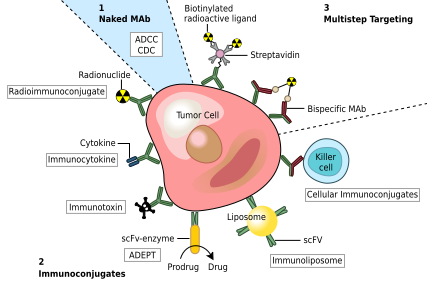
Structure of eculizumab. Eculizumab was engineered
to reduce immunogenicity and eliminate effector function. Human IgG2 and IgG4
heavy-chain sequences were combined to form a hybrid constant region that is
unable to bind Fc receptors or to activate the complement cascade. Eculizumab
exhibits high affinity for human C5, effectively blocking its cleavage and
downstream proinflammatory and cell lytic properties. Reprinted from Rother et
al with permission.
Alexion's Soliris® (eculizumab) Receives Orphan Drug Designation for the ...
Fort Mills Times
In a Phase 2 study presented at the 2012 annual meeting of the American Neurological Association (ANA), Soliris treatment was associated with a significant reduction in the frequency of relapses (recurring attacks) in patients with severe, relapsing ...
http://www.fortmilltimes.com/2013/06/27/2789656/alexions-soliris-eculizumab-receives.html
Eculizumab (INN and USAN; trade name Soliris) is a humanized monoclonal antibody that is a first-in-class terminal complement inhibitor and the first therapy approved for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), a rare, progressive, and sometimes life-threatening disease characterized by excessive destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis). It costs £400,000 (US$600,000) per year per patient
Eculizumab also is the first agent approved for the treatment of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), an ultra-rare genetic disease that causes abnormal blood clots to form in small blood vessels throughout the body, leading to kidney failure, damage to other vital organs and premature death.
In clinical trials in patients with PNH, eculizumab was associated with reductions in chronic hemolysis, thromboembolic events, and transfusion requirements, as well as improvements in PNH symptoms, quality of life, and survival.Clinical trials in patients with aHUS demonstrated inhibition of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA),the formation of blood clots in small blood vessels throughout the body, including normalization of platelets and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), as well as maintenance or improvement in renal function.
Eculizumab was discovered and developed by Alexion Pharmaceuticals and is manufactured by Alexion. It was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on March 16, 2007 for the treatment of PNH, and on September 23, 2011 for the treatment of aHUS. It was approved by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of PNH on June 20, 2007, and on November 24, 2011 for the treatment of aHUS. Eculizumab is currently being investigated as a potential treatment for other severe, ultra-rare disorders.




 A new peptidomimetic inhibits prostate cancer’s growth by
preventing the androgen receptor from binding to its cofactor
A new peptidomimetic inhibits prostate cancer’s growth by
preventing the androgen receptor from binding to its cofactor